Managing Russian Bees Russian
“The primary purpose of the corporation will be to maintain and improve the genetic lines of Russian honey bees through propagation and selective breeding.”
Varroa also may pass between colonies in other ways. First, beekeepers often aid weak colonies by adding bees or brood from a healthier colony, and this practice

Russian sage plants (Perovskia atriplicifolia) are treated as perennials but are woody sub-shrubs. Perovskia has silver leaves and tall flower spikes.

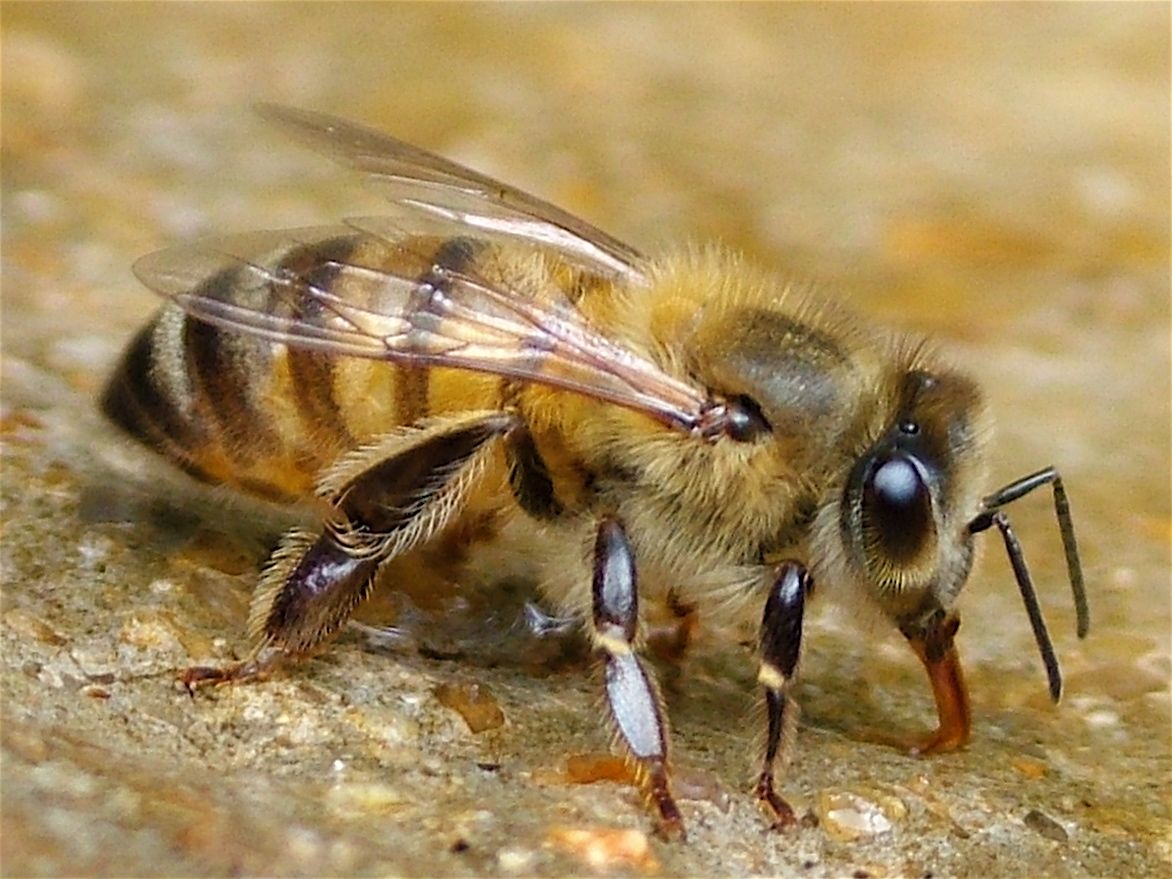
Beekeeping has become increasingly popular in New York City. Although generally docile, honeybees (Apis mellifera) can and may sting. Responsible management is

Get the latest technology news and video about mobile devices, technology trends, the internet, privacy and more.


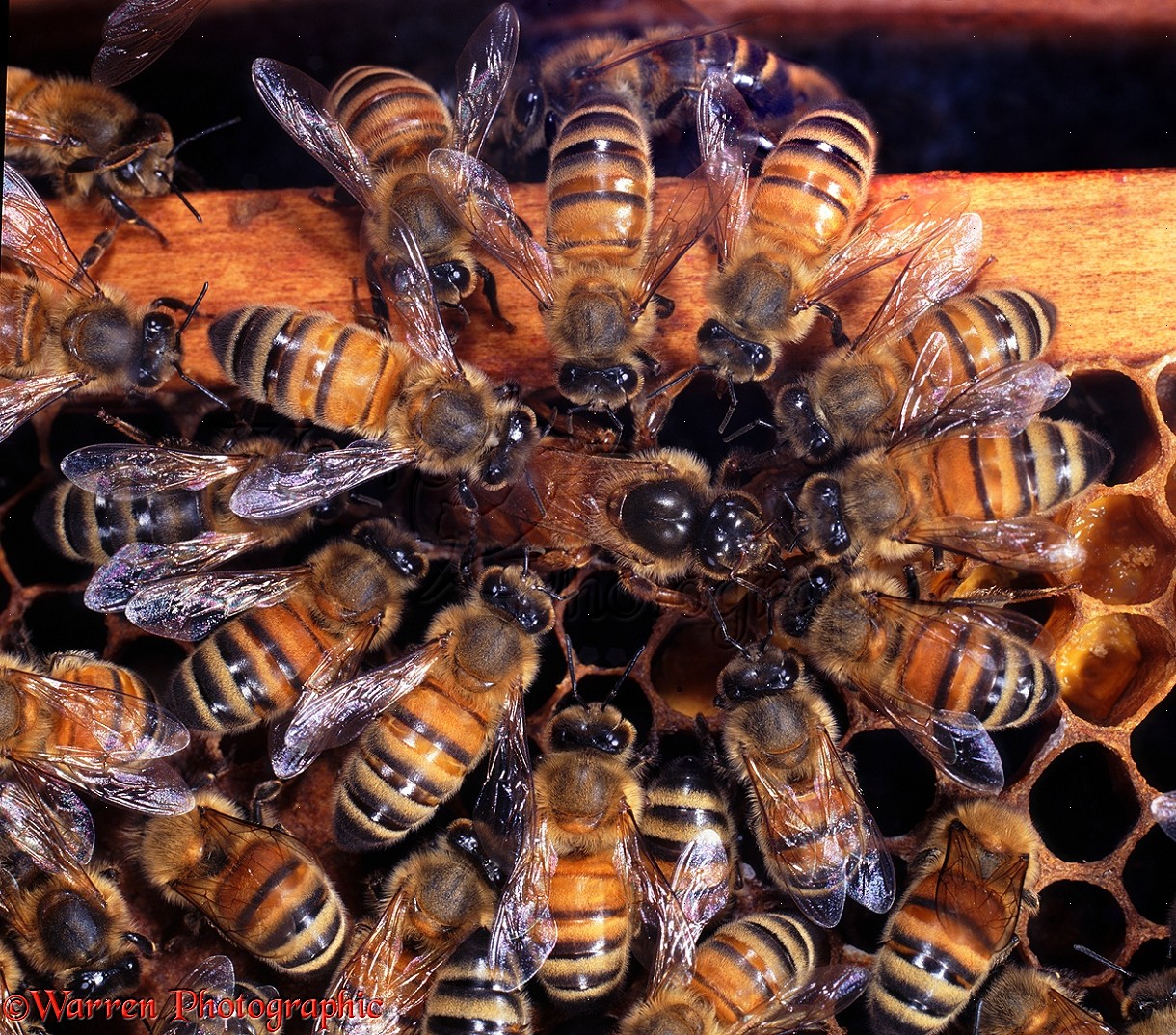
IPM 2 Fighting Varroa 2: Choosing your Troops: Breeding Mite-Fighting Bees

Our Carniolan queen bees are raised from our own breeding stock. We have had very good success with these homegrown queens.

Grain growers are advised to monitor their crops for infestations of the newly introduced Russian wheat aphid and to report suspected infestations but to hold off

Breeding, Genetics, Stock Improvement and Management of Russian Honey Bees for Mite and Small Hive Beetle Control and Pollination, Research project Number: 6413-21000
What’s Happening To The Bees? – Part 5: Is There A Difference Between Domesticated And Feral Bees?
